Advanced Laboratories
Committed to promoting the integration of multi-disc iplinary approaches for Chinese medicines identification, GCMTI is equipped with advanced and internationally recognised laboratories to embark on high-tech scientific research and develop testing methods. The methods so developed will be transferred for the use of the public, the Chinese medicines sector as well as the testing sector with a view to strengthening the capability for quality control and identification of Chinese medicines.
Macroscopic Identification Laboratory
Macroscopic Identification Laboratory is functionally divided into several areas, including a sample reception room, a sample weighing room, a sample temporary storage room, a sample preparation room, and the macroscopic identification laboratory.
The laboratory is equipped with high-resolution digital cameras and professional lighting equipment. The high-fidelity images captured not only accurately record the characteristics of the samples but also aid in the teaching and dissemination of macroscopic identification techniques. The laboratory is also responsible for developing standards and building a knowledge base for “micro-morphological identification”. This methodology, which involves using stereomicroscope to magnify tiny features of samples that are difficult to detect or see clearly with the naked eye, provides more reliable evidence for Chinese materia medica samples identification.
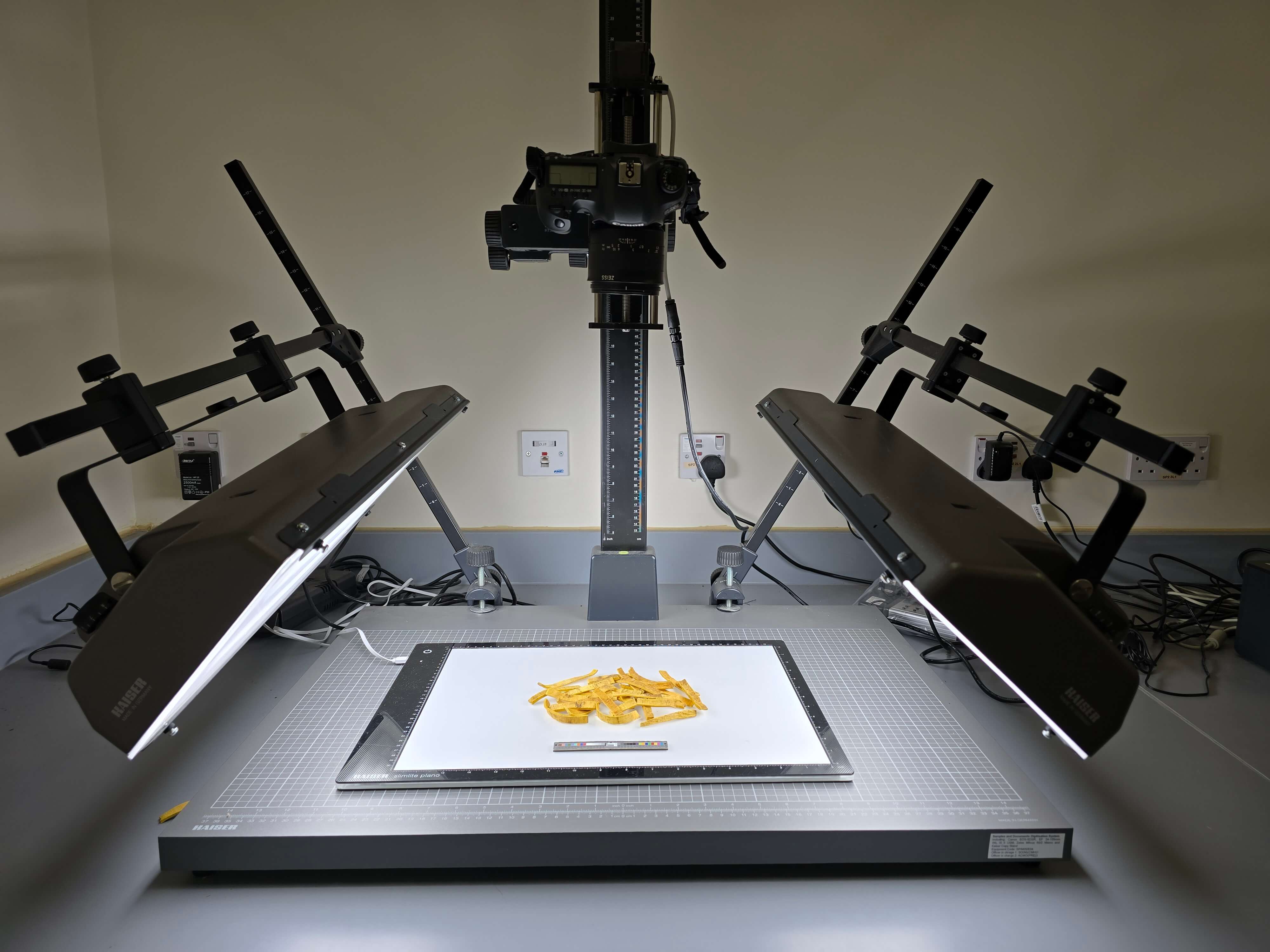

Microscopic Identification Laboratory
Microscopic Identification Laboratory not only sets conventional microscopic identification standards but has also developed the “Simplified Powder Microscopic Identification” method. This innovative method offers a straightforward and accurate way to identify cortex type of decoction pieces that have few and similar macroscopic features. This method requires only a portable microscope and basic tools, allowing for widespread use in the field.
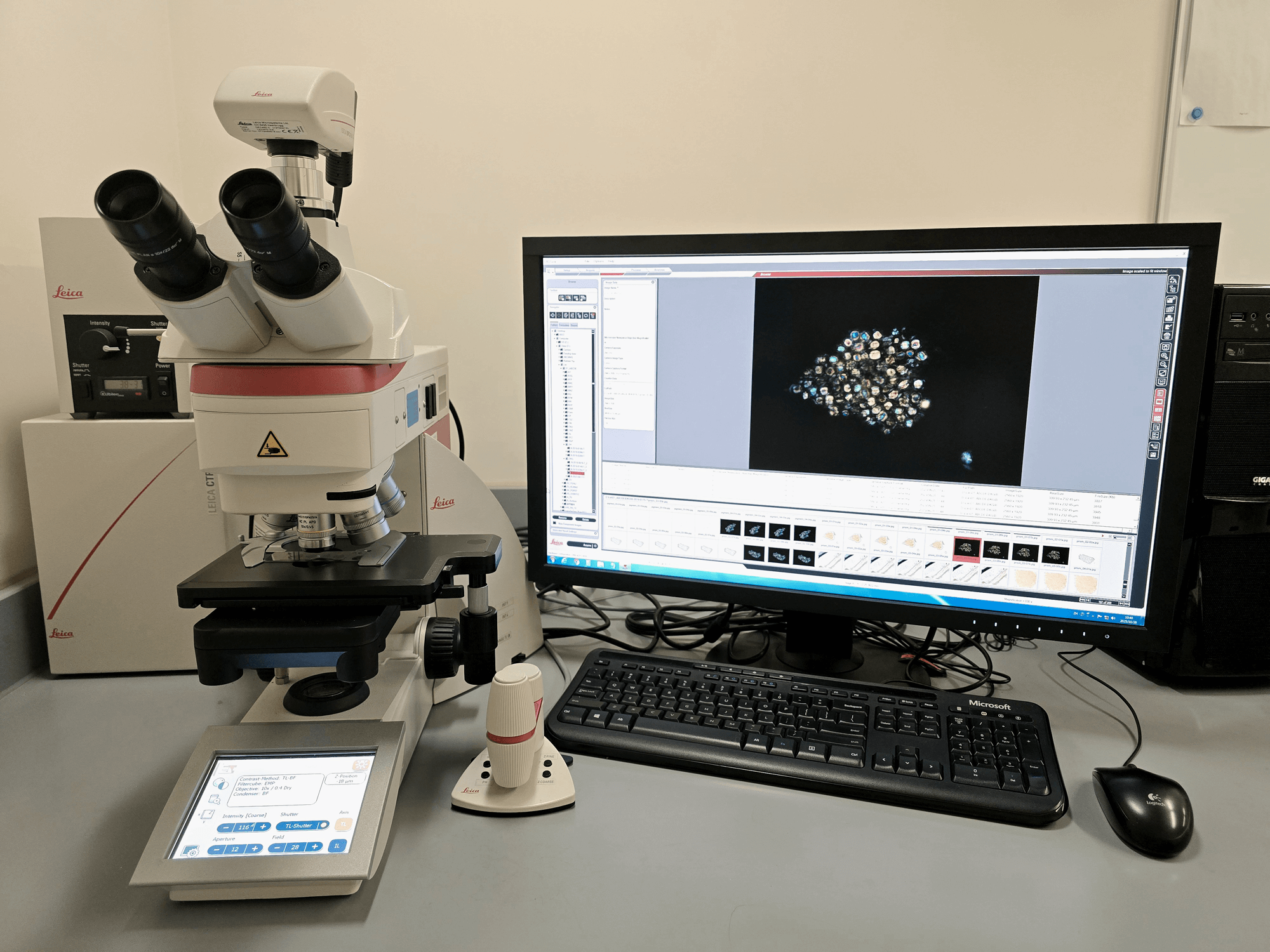
Advanced Pharmacognostic Laboratory
The GCMTI actively applies new equipment and modern technologies into traditional identification methods, achieving a fusion of traditional techniques and modern science. The newly established Advanced Pharmacognostic Laboratory features specialised facilities, including an electronic nose analysis room, an electronic tongue analysis room, a colour and shade analysis room, a computer-aided identification room. Equipped with advanced electronic sensory analysis instruments, the laboratory supports sophisticated analysis of Chinese medicines. The application of these advanced technologies to Chinese medicines will further advance the modernisation and standardisation of Chinese medicines identification and quality control methods.

Chemistry Laboratory


DNA Laboratory


(Sanger Sequencing)