Chinese Medicine Regulatory Office
Site Menu
Chinese Medicines Herbarium

Government Chinese Medicines Testing Institute
Chinese Medicines Herbarium

Background
In the 2015 Policy Address, the Government announced the planning and
development of a testing centre for Chinese medicines to be managed by the Department of Health. The testing
centre, now named as the Government Chinese Medicines Testing Institute (GCMTI), will specialise in the testing
of, and scientific research on, Chinese medicines with a view to setting internationally recognised reference
standards for the safety, quality and testing methods of Chinese medicines. Pending the establishment of the
permanent GCMTI, a temporary institute has been set up in the Hong Kong Science Park and has commenced operation
in phases from March 2017.
Traditional Chinese medicine is a treasure of the Chinese nation, which
embodies the essence of the Chinese traditional culture. As Chinese medicines constitute an important part of
traditional Chinese medicine, Chinese Medicines Herbarium has been set up in the GCMTI in the Science Park with
an aim to promote the development of Chinese medicine in Hong Kong by collecting and managing of Chinese
medicines and Lingnan herbal medicines specimens, as well as providing physical specimens for comparative
identification and studies.

We hope that Chinese Medicines Herbarium can support the research and testing of Chinese medicines via the collection and management of various specimens of Chinese medicines and other traditional herbs, as well as to promote public knowledge of Chinese medicines through display of specimens.
Functions
- To provide authoritative specimens and to promote the research of Chinese medicines through the collection of medicinal materials specimens with their corresponding source plants specimens and microscopic slides; and
- To give public a better understanding of Chinese medicine and to inherit culture of Chinese medicine.
Plants Specimens
Medicinal Materials Specimens
Microscopic Slides
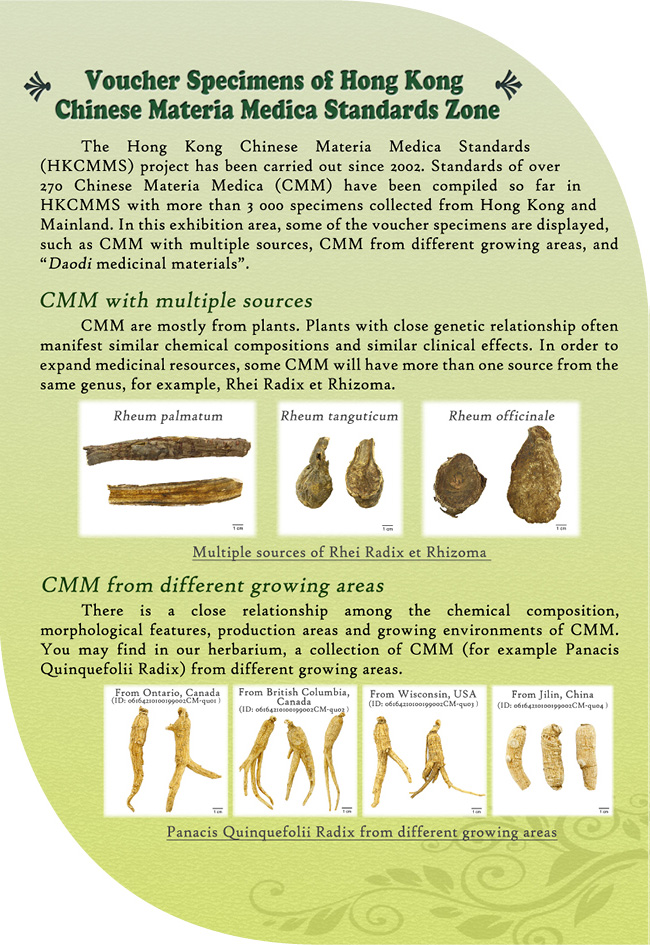
Voucher Specimens of Hong Kong Chinese Materia Medica Standards Zone
The Hong Kong Chinese Materia Medica Standards (HKCMMS) project has been carried out since 2002. Standards of over 270 Chinese Materia Medica (CMM) have been compiled so far in HKCMMS with more than 3 000 specimens collected from Hong Kong and Mainland. In this exhibition area, some of the voucher specimens are displayed, such as CMM with multiple sources, CMM from different growing areas, and “Daodi medicinal materials”.
CMM with multiple sources
CMM are mostly from plants. Plants with close genetic
relationship often manifest similar chemical compositions and similar clinical effects. In order to expand
medicinal resources, some CMM will have more than one source from the same genus, for example, Rhei Radix et
Rhizoma.
Multiple-sources of Rhei Radix et Rhizoma
Rheum palmatum Rheum tanguticum Rheum
officinale
CMM from different growing areas
There is a close relationship among the chemical
composition, morphological features, production areas and growing environments of CMM. You may find in our
herbarium, a collection of CMM (for example Panacis Quinquefolii Radix) from different growing areas.
Panacis Quinquefolii Radix from different growing areas
From Ontario, Canada (ID:
06164210100199002CM-qu01)
From British Columbia, Canada (ID: 06164210100199002CM-qu02)
From
Wisconsin, USA (ID: 06164210100199002CM-qu03)
From Jilin, China (ID: 06164210100199002CM-qu04)

Chinese Materia Medica Specimens Donated by National Medical Products Administration
The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) and its affiliated institution, National Institutes for Food and Drug Control offer technical advice and opinions to the establishment of the Chinese Medicines Herbarium. They have also arranged to gift precious and representative specimens of commonly used CMM to the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government. Some of the specimens have been on display at the GCMTI since 2019, including a set of cordyceps showcasing different growth stages and specimens from various production regions.
Lingnan Herbal Medicines Zone
Lingnan herbal medicines refer to herbal medicines which
are produced in Guangdong, Guangxi and Hainan provinces etc., commonly used by Lingnan local peoples. A majority
of samples displayed in this exhibition area are collected by our staff from Hong Kong's countryside after
obtaining a licence from Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department (AFCD).

Featured Showcase
Hong Kong was once a famous trade port of Agarwood, hence it is
believed that Hong Kong (which means “Incense Harbour”) had derived its name from it. Agarwood, a famous and
precious Chinese medicines, is the resin-containing wood of Aquilaria species (Thymelaeaceae). The trade in wild
Agarwood is now controlled by the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and
Flora. Specimens of Agarwood (a courtesy of AFCD) are now displayed in our Chinese Medicines Herbarium, as a
remembrance of the indissoluble bonding between Agarwood and Hong Kong.
Apart from Agarwood, some other
wild sources of Chinese medicines have also become endangered due to destruction of their habitat or being
over-exploited. Also displayed in the featured showcase are specimens donated by AFCD, including rhinoceros
horns, an antelope horn and scales of pangolin to promote awareness on the protection and sustainable use of
Chinese medicines resources.
Over 3 300 plants species have been found in Hong Kong with at least 16 of
them being first discovered in Hong Kong and hence named after it. In the lower section of the showcase, eight
watercolour paintings (drawn by a local artist) of species which were named after Hong Kong are displayed, to
reflect the unique characteristics of Hong Kong.
Asarum hongkongense (left) & Aristolochia
westlandii (right)

Thematic Showcases
This zone shows different thematic subjects regularly, including ingredients of traditional herbal teas, various specifications of Angelicae Sinensis Radix and its decoction pieces, famous and precious Chinese medicines, easily confused Chinese medicines and Western herbal medicines. Specimens of Southeast Asia Herbal Medicines are now on display, please refer to relevant pages for details.

Contact Us
Address: 7/F, BioTech Centre 2, 11 Science Park West Avenue, Phase 2, Hong
Kong Science Park, Shatin, N.T.
Tel: 2209 9476
E-mail: gcmti_herbarium@dh.gov.hk
Location
By Public Transport:Kowloon Motor Bus 272K, 272S, 43P, 74D, 74P Green minibus No. 27
By Car: Pak Shek Kok
Entrance to Hong Kong Science Park
GCMTI’s website